- Senegal
-
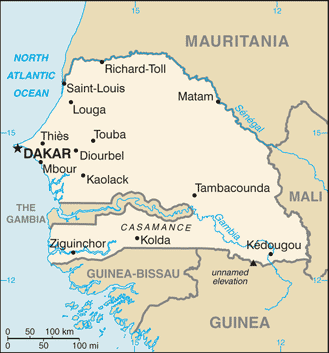 Introduction ::SenegalBackground:The French colonies of Senegal and the French Sudan were merged in 1959 and granted their independence as the Mali Federation in 1960. The union broke up after only a few months. Senegal joined with The Gambia to form the nominal confederation of Senegambia in 1982. The envisaged integration of the two countries was never carried out, and the union was dissolved in 1989. The Movement of Democratic Forces in the Casamance (MFDC) has led a low-level separatist insurgency in southern Senegal since the 1980s, and several peace deals have failed to resolve the conflict. Nevertheless, Senegal remains one of the most stable democracies in Africa and has a long history of participating in international peacekeeping and regional mediation. Senegal was ruled by a Socialist Party for 40 years until Abdoulaye WADE was elected president in 2000. He was reelected in 2007 and during his two terms amended Senegal's constitution over a dozen times to increase executive power and to weaken the opposition. His decision to run for a third presidential term sparked a large public backlash that led to his defeat in a March 2012 runoff election with Macky SALL.Geography ::SenegalLocation:Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Guinea-Bissau and MauritaniaGeographic coordinates:14 00 N, 14 00 WArea:total: 196,722 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 88land: 192,530 sq kmwater: 4,192 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly smaller than South DakotaLand boundaries:total: 2,640 kmborder countries: The Gambia 740 km, Guinea 330 km, Guinea-Bissau 338 km, Mali 419 km, Mauritania 813 kmCoastline:531 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental marginClimate:tropical; hot, humid; rainy season (May to November) has strong southeast winds; dry season (December to April) dominated by hot, dry, harmattan windTerrain:generally low, rolling, plains rising to foothills in southeastElevation extremes:lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 mhighest point: unnamed elevation southwest of Kedougou 581 mNatural resources:fish, phosphates, iron oreLand use:arable land: 19.57%permanent crops: 0.28%other: 80.15% (2011)Irrigated land:1,197 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:38.8 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 2.22 cu km/yr (4%/3%/93%)per capita: 221.6 cu m/yr (2002)Natural hazards:lowlands seasonally flooded; periodic droughtsEnvironment - current issues:wildlife populations threatened by poaching; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification; overfishingEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:westernmost country on the African continent; The Gambia is almost an enclave within SenegalPeople and Society ::SenegalNationality:noun: Senegalese (singular and plural)adjective: SenegaleseEthnic groups:Wolof 43.3%, Pular 23.8%, Serer 14.7%, Jola 3.7%, Mandinka 3%, Soninke 1.1%, European and Lebanese 1%, other 9.4%Languages:French (official), Wolof, Pulaar, Jola, MandinkaReligions:Muslim 94%, Christian 5% (mostly Roman Catholic), indigenous beliefs 1%Population:13,300,410 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Age structure:0-14 years: 42.7% (male 2,855,431/female 2,828,107)15-24 years: 20.5% (male 1,357,979/female 1,372,107)25-54 years: 30.1% (male 1,825,507/female 2,182,110)55-64 years: 3.7% (male 218,512/female 277,047)65 years and over: 2.9% (male 174,946/female 208,664) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 86.9 %youth dependency ratio: 81.3 %elderly dependency ratio: 5.6 %potential support ratio: 17.9 (2013)Median age:total: 18.2 yearsmale: 17.4 yearsfemale: 19.1 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:2.51% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Birth rate:35.64 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 25Death rate:8.85 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Net migration rate:-1.74 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 156Urbanization:urban population: 42.5% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 3.32% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:DAKAR (capital) 2.777 million (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.99 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.83 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.8 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.85 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.94 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:21.4note: Median age at first birth among women 25-29 (2011 est.)Maternal mortality rate:370 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 28Infant mortality rate:total: 53.93 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 36male: 60.22 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 47.44 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 60.57 yearscountry comparison to the world: 192male: 58.58 yearsfemale: 62.61 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:4.61 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 27Contraceptive prevalence rate:13.1% (2010/11)Health expenditures:5.7% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 116Physicians density:0.06 physicians/1,000 population (2008)Hospital bed density:0.34 beds/1,000 population (2008)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 93% of populationrural: 56% of populationtotal: 72% of populationunimproved:urban: 7% of populationrural: 44% of populationtotal: 28% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 70% of populationrural: 39% of populationtotal: 52% of populationunimproved:urban: 30% of populationrural: 61% of populationtotal: 48% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.9% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 51HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:59,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 56HIV/AIDS - deaths:2,600 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 50Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: very highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: dengue fever, malaria, and yellow feverwater contact disease: schistosomiasisrespiratory disease: meningococcal meningitisanimal contact disease: rabies (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:6.8% (2008)country comparison to the world: 145Children under the age of 5 years underweight:19.2% (2011)country comparison to the world: 37Education expenditures:5.6% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 50Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 49.7%male: 61.8%female: 38.7% (2009 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 8 yearsmale: 8 yearsfemale: 8 years (2010)Child labor - children ages 5-14:total number: 657,216percentage: 22 % (2005 est.)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 14.8%country comparison to the world: 85male: 11.9%female: 20.1% (2006)Government ::SenegalCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Senegalconventional short form: Senegallocal long form: Republique du Senegallocal short form: Senegalformer: Senegambia (along with The Gambia), Mali FederationGovernment type:republicCapital:name: Dakargeographic coordinates: 14 44 N, 17 38 Wtime difference: UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:14 regions (regions, singular - region); Dakar, Diourbel, Fatick, Kaffrine, Kaolack, Kedougou, Kolda, Louga, Matam, Saint-Louis, Sedhiou, Tambacounda, Thies, ZiguinchorIndependence:4 April 1960 (from France); note - complete independence achieved upon dissolution of federation with Mali on 20 August 1960National holiday:Independence Day, 4 April (1960)Constitution:adopted 7 January 2001; amended many timesLegal system:civil law system based on French law; judicial review of legislative acts in Constitutional CourtInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Macky SALL (since 2 April 2012)head of government: Prime Minister Aminata TOURE (since 3 September 2013)cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the prime minister in consultation with the president(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by popular vote for a seven-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 26 February 2012 with a second round runoff on 25 March 2012 (next to be held 2019); prime minister appointed by the presidentelection results: Macky SALL elected president; percent of votes in a runoff - Macky SALL 65.8%, Abdoulaye WADE 34.2%Legislative branch:unicameral National Assembly or Assemblee Nationale (150 seats; 90 members elected by direct popular vote and 60 elected by proportional representation from party lists to serve five-year terms)elections: National Assembly - last held on 1 July 2012 (next to be held in 2017)election results: National Assembly results - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Benno Bokk Yakaar coalition 119, PDS 12, Bokk Giss Giss coalition 4, MCRN-Bes Du Nakk 4, PVD 2, MRDS 2, URD 1, AJ/PADS 1, other 5Judicial branch:highest court(s): Highest Appeals Court or Cour de Cassation (consists of 13 judges including the court president); Constitutional Council (consists of 5 members including the court president, vice-president, and 3 judges)judge selection and term of office: Highest Appeals Court judges' tenure NA; Constitutional Council members appointed by the president of the republic to serve 6-year terms with renewal of 3 members every two yearssubordinate courts: Court of Appeals; regional and first instance courtsPolitical parties and leaders:African Party of Independence [Majhemout DIOP]Alliance for the Republic-Yakaar [Macky SALL]Alliance of Forces of Progress or AFP [Moustapha NIASSE]And-Jef/African Party for Democracy and Socialism or AJ/PADS [Landing SAVANE]Benno Bokk Yakaar coaltion [Macky SALL]Benno Siggil Senegal (a coalition of opposition parties)Bokk Giss Giss coalition [Pape DIOP]Citizen Movement for National Reform or MCRN-Bes Du NakkDemocratic League-Labor Party Movement or LD-MPT [Dr. Abdoulaye BATHILY]Front for Socialism and Democracy/Benno Jubel or FSD/BJ [Cheikh Abdoulaye Bamba DIEYE]Gainde Centrist Bloc or BGC [Jean-Paul DIAS]Independence and Labor Party or PIT [Amath DANSOKHO]Jef-Jel [Talla SYLLA]National Democratic Rally or RND [Madior DIOUF]Party for Truth and Development or PVD [Ahmadou Kara MBACKE]People's Labor Party or PTP [El Hadji DIOUF]Reform Party or PR [Abdourahim AGNE]Republican Movement for Socialism and Democracy or MRDSRewmi Party [Idrissa SECK]Senegalese Democratic Party or PDS [Abdoulaye WADE]Socialist Party or PS [Ousmane Tanor DIENG]SOPI Coalition [Abdoulaye WADE] (a coalition led by the PDS)Synergy for Ethics and Transparency [Aminata TALL]Union for Democratic Renewal or URD [Djibo Leyti KA]Political pressure groups and leaders:other: labor; students; Sufi brotherhoods, including the Mourides and Tidjanes; teachersInternational organization participation:ACP, AfDB, AU, CD, CPLP (associate), ECOWAS, FAO, FZ, G-15, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WADB (regional), WAEMU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Cheikh NIANGchancery: 2031 Florida Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20009telephone: [1] (202) 234-0540FAX: [1] (202) 332-6315consulate(s) general: Houston, New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Lewis LUKENSembassy: Route des Almadies, Dakarmailing address: B. P. 49, Dakartelephone: [221] 33-879-4000FAX: [221] 33-822-2991Flag description:three equal vertical bands of green (hoist side), yellow, and red with a small green five-pointed star centered in the yellow band; green represents Islam, progress, and hope; yellow signifies natural wealth and progress; red symbolizes sacrifice and determination; the star denotes unity and hopenote: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia; the colors from left to right are the same as those of neighboring Mali and the reverse of those on the flag of neighboring GuineaNational symbol(s):lionNational anthem:name: ""Pincez Tous vos Koras, Frappez les Balafons"" (Pluck Your Koras, Strike the Balafons)lyrics/music: Leopold Sedar SENGHOR/Herbert PEPPERnote: adopted 1960; the lyrics were written by Leopold Sedar SENGHOR, Senegal's first president; the anthem is sometimes played incorporating the Koras (harp-like stringed instruments) and Balafons (types of xylophones) mentioned in the titleEconomy ::SenegalEconomy - overview:Senegal relies heavily on donor assistance and foreign direct investment. The country's key export industries are phosphate mining, fertilizer production, and commercial fishing. The country is also working on iron ore and oil exploration projects. After seeing its economy contract by 2.1% in 1993, Senegal made an important turnaround, thanks to an economic reform program backed by the donor community, which led to real growth in GDP averaging over 5% annually during 1995-2007. Annual inflation was pushed down to the single digits. The global economic downturn reduced growth to 2.2% in 2009. The IMF completed a non-dispersing, Policy Support Initiative program in 2010 and approved a new three-year policy support instrument in December 2010 to assist with economic reforms. Senegal also receives disbursements from a $540 million Millennium Challenge Account for infrastructure and agriculture development. In 2012, the economy began to rebound after a weak 2011. The economy continues to suffer from unreliable power supply, which has led to public protests and high unemployment and has prompted migrants to flee Senegal in search of better job opportunities in Europe.GDP (purchasing power parity):$27.01 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 118$26.09 billion (2011 est.)$25.42 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$13.86 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:3.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 972.6% (2011 est.)4.3% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$2,100 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 193$2,000 (2011 est.)$2,000 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:16.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9217.5% of GDP (2011 est.)21.4% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 80.2%government consumption: 6.9%investment in fixed capital: 25.5%investment in inventories: 4.2%exports of goods and services: 28.4%imports of goods and services: -45.1%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 15.2%industry: 22.6%services: 62.2% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:peanuts, millet, corn, sorghum, rice, cotton, tomatoes, green vegetables; cattle, poultry, pigs; fishIndustries:agricultural and fish processing, phosphate mining, fertilizer production, petroleum refining; iron ore, zircon, and gold mining, construction materials, ship construction and repairIndustrial production growth rate:0.1% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 133Labor force:5.906 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 77.5%industry and services: 22.5% (2007 est.)Unemployment rate:48% (2007 est.)country comparison to the world: 193Population below poverty line:54% (2001 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 2.5%highest 10%: 30.1% (2005)Distribution of family income - Gini index:41.3 (2001)country comparison to the world: 5441.3 (1995)Budget:revenues: $3.359 billionexpenditures: $4.213 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:24.2% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 131Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-6.2% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 180Public debt:36.1% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 10035.6% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):1.4% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 253.4% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:0.25% (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 904.25% (31 December 2009 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:14.3% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 4914.5% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$3.577 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 108$3.254 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$5.818 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 122$5.35 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$4.509 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 121$4.186 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$NACurrent account balance:-$1.298 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 120-$1.685 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$2.382 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 138$2.413 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:fish, groundnuts (peanuts), petroleum products, phosphates, cottonExports - partners:Mali 14.4%, Switzerland 14.1%, India 11.9%, France 4.7%, Guinea 4.2% (2012)Imports:$5.733 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 124$5.392 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:food and beverages, capital goods, fuelsImports - partners:France 16.2%, Nigeria 12.9%, India 6.3%, China 6.3%, UK 4.6% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$2.082 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 120$1.946 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$4.222 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 128$4.32 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XOF) per US dollar -510.53 (2012 est.)471.87 (2011 est.)495.28 (2010)472.19 (2009)447.81 (2008)Energy ::SenegalElectricity - production:2.608 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 130Electricity - consumption:2.123 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 139Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 126Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 129Electricity - installed generating capacity:638,000 kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 130Electricity - from fossil fuels:99.7% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 173Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 196Electricity - from other renewable sources:0.3% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 81Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 179Crude oil - imports:13,040 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 183Refined petroleum products - production:16,850 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 97Refined petroleum products - consumption:40,600 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 108Refined petroleum products - exports:7,046 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Refined petroleum products - imports:16,700 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 110Natural gas - production:50 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Natural gas - consumption:50 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 108Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 175Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 126Natural gas - proved reserves:NA cu mCarbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:6.679 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 113Communications ::SenegalTelephones - main lines in use:346,400 (2011)country comparison to the world: 110Telephones - mobile cellular:9.353 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 79Telephone system:general assessment: good system with microwave radio relay, coaxial cable and fiber-optic cable in trunk systemdomestic: above-average urban system with a fiber-optic network; nearly two-thirds of all fixed-line connections are in Dakar where a call-center industry is emerging; expansion of fixed-line services in rural areas needed; mobile-cellular service is expanding rapidlyinternational: country code - 221; the SAT-3/WASC fiber-optic cable provides connectivity to Europe and Asia while Atlantis-2 provides connectivity to South America; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2010)Broadcast media:state-run Radiodiffusion Television Senegalaise (RTS) operates 2 TV stations; a few private TV subscription channels rebroadcast foreign channels without providing any local news or programs; RTS operates a national radio network and a number of regional FM stations; many community and private-broadcast radio stations are available; transmissions of at least 2 international broadcasters are accessible on FM in Dakar (2007)Internet country code:.snInternet hosts:237 (2012)country comparison to the world: 197Internet users:1.818 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 76Transportation ::SenegalAirports:20 (2013)country comparison to the world: 136Airports - with paved runways:total: 9over 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 6914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 111,524 to 2,437 m: 7914 to 1,523 m: 3under 914 m:1 (2013)Pipelines:gas 43 km; refined products 8 km (2013)Railways:total: 906 kmcountry comparison to the world: 92narrow gauge: 906 km 1.000-m gauge (2008)Roadways:total: 14,008 kmcountry comparison to the world: 124paved: 4,099 km (includes 7 km of expressways)unpaved: 9,909 km (2003)Waterways:1,000 km (primarily on the Senegal, Saloum, and Casamance rivers) (2012)country comparison to the world: 64Merchant marine:total: 1country comparison to the world: 150by type: passenger/cargo 1 (2010)Ports and terminals:DakarMilitary ::SenegalMilitary branches:Senegalese Armed Forces: Army, Senegalese National Navy (Marine Senegalaise, MNS), Senegalese Air Force (Armee de l'Air du Senegal) (2013)Military service age and obligation:18 years of age for voluntary military service; 20 years of age for selective conscript service; service obligation is 2 years; women have been accepted into military service since 2008 (2013)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 2,699,196females age 16-49: 3,018,565 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 1,788,493females age 16-49: 2,133,370 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 145,509female: 145,064 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:1.6% of GDP (2011)country comparison to the world: 89Transnational Issues ::SenegalDisputes - international:The Gambia and Guinea-Bissau attempt to stem separatist violence, cross border raids, and arms smuggling into their countries from Senegal's Casamance region, and in 2006, respectively accepted 6,000 and 10,000 Casamance residents fleeing the conflict; 2,500 Guinea-Bissau residents fled into Senegal in 2006 to escape armed confrontations along the borderRefugees and internally displaced persons:refugees (country of origin): 13,702 (Mauritania) (2012)IDPs: 10,000-40,000 (clashes between government troops and separatists in Casamance region) (2012)Illicit drugs:transshipment point for Southwest and Southeast Asian heroin and South American cocaine moving to Europe and North America; illicit cultivator of cannabis"
Introduction ::SenegalBackground:The French colonies of Senegal and the French Sudan were merged in 1959 and granted their independence as the Mali Federation in 1960. The union broke up after only a few months. Senegal joined with The Gambia to form the nominal confederation of Senegambia in 1982. The envisaged integration of the two countries was never carried out, and the union was dissolved in 1989. The Movement of Democratic Forces in the Casamance (MFDC) has led a low-level separatist insurgency in southern Senegal since the 1980s, and several peace deals have failed to resolve the conflict. Nevertheless, Senegal remains one of the most stable democracies in Africa and has a long history of participating in international peacekeeping and regional mediation. Senegal was ruled by a Socialist Party for 40 years until Abdoulaye WADE was elected president in 2000. He was reelected in 2007 and during his two terms amended Senegal's constitution over a dozen times to increase executive power and to weaken the opposition. His decision to run for a third presidential term sparked a large public backlash that led to his defeat in a March 2012 runoff election with Macky SALL.Geography ::SenegalLocation:Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Guinea-Bissau and MauritaniaGeographic coordinates:14 00 N, 14 00 WArea:total: 196,722 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 88land: 192,530 sq kmwater: 4,192 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly smaller than South DakotaLand boundaries:total: 2,640 kmborder countries: The Gambia 740 km, Guinea 330 km, Guinea-Bissau 338 km, Mali 419 km, Mauritania 813 kmCoastline:531 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental marginClimate:tropical; hot, humid; rainy season (May to November) has strong southeast winds; dry season (December to April) dominated by hot, dry, harmattan windTerrain:generally low, rolling, plains rising to foothills in southeastElevation extremes:lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 mhighest point: unnamed elevation southwest of Kedougou 581 mNatural resources:fish, phosphates, iron oreLand use:arable land: 19.57%permanent crops: 0.28%other: 80.15% (2011)Irrigated land:1,197 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:38.8 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 2.22 cu km/yr (4%/3%/93%)per capita: 221.6 cu m/yr (2002)Natural hazards:lowlands seasonally flooded; periodic droughtsEnvironment - current issues:wildlife populations threatened by poaching; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification; overfishingEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:westernmost country on the African continent; The Gambia is almost an enclave within SenegalPeople and Society ::SenegalNationality:noun: Senegalese (singular and plural)adjective: SenegaleseEthnic groups:Wolof 43.3%, Pular 23.8%, Serer 14.7%, Jola 3.7%, Mandinka 3%, Soninke 1.1%, European and Lebanese 1%, other 9.4%Languages:French (official), Wolof, Pulaar, Jola, MandinkaReligions:Muslim 94%, Christian 5% (mostly Roman Catholic), indigenous beliefs 1%Population:13,300,410 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Age structure:0-14 years: 42.7% (male 2,855,431/female 2,828,107)15-24 years: 20.5% (male 1,357,979/female 1,372,107)25-54 years: 30.1% (male 1,825,507/female 2,182,110)55-64 years: 3.7% (male 218,512/female 277,047)65 years and over: 2.9% (male 174,946/female 208,664) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 86.9 %youth dependency ratio: 81.3 %elderly dependency ratio: 5.6 %potential support ratio: 17.9 (2013)Median age:total: 18.2 yearsmale: 17.4 yearsfemale: 19.1 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:2.51% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Birth rate:35.64 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 25Death rate:8.85 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Net migration rate:-1.74 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 156Urbanization:urban population: 42.5% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 3.32% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:DAKAR (capital) 2.777 million (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.99 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.83 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.8 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.85 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.94 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:21.4note: Median age at first birth among women 25-29 (2011 est.)Maternal mortality rate:370 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 28Infant mortality rate:total: 53.93 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 36male: 60.22 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 47.44 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 60.57 yearscountry comparison to the world: 192male: 58.58 yearsfemale: 62.61 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:4.61 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 27Contraceptive prevalence rate:13.1% (2010/11)Health expenditures:5.7% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 116Physicians density:0.06 physicians/1,000 population (2008)Hospital bed density:0.34 beds/1,000 population (2008)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 93% of populationrural: 56% of populationtotal: 72% of populationunimproved:urban: 7% of populationrural: 44% of populationtotal: 28% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 70% of populationrural: 39% of populationtotal: 52% of populationunimproved:urban: 30% of populationrural: 61% of populationtotal: 48% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.9% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 51HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:59,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 56HIV/AIDS - deaths:2,600 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 50Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: very highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: dengue fever, malaria, and yellow feverwater contact disease: schistosomiasisrespiratory disease: meningococcal meningitisanimal contact disease: rabies (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:6.8% (2008)country comparison to the world: 145Children under the age of 5 years underweight:19.2% (2011)country comparison to the world: 37Education expenditures:5.6% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 50Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 49.7%male: 61.8%female: 38.7% (2009 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 8 yearsmale: 8 yearsfemale: 8 years (2010)Child labor - children ages 5-14:total number: 657,216percentage: 22 % (2005 est.)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 14.8%country comparison to the world: 85male: 11.9%female: 20.1% (2006)Government ::SenegalCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Senegalconventional short form: Senegallocal long form: Republique du Senegallocal short form: Senegalformer: Senegambia (along with The Gambia), Mali FederationGovernment type:republicCapital:name: Dakargeographic coordinates: 14 44 N, 17 38 Wtime difference: UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:14 regions (regions, singular - region); Dakar, Diourbel, Fatick, Kaffrine, Kaolack, Kedougou, Kolda, Louga, Matam, Saint-Louis, Sedhiou, Tambacounda, Thies, ZiguinchorIndependence:4 April 1960 (from France); note - complete independence achieved upon dissolution of federation with Mali on 20 August 1960National holiday:Independence Day, 4 April (1960)Constitution:adopted 7 January 2001; amended many timesLegal system:civil law system based on French law; judicial review of legislative acts in Constitutional CourtInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Macky SALL (since 2 April 2012)head of government: Prime Minister Aminata TOURE (since 3 September 2013)cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the prime minister in consultation with the president(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by popular vote for a seven-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 26 February 2012 with a second round runoff on 25 March 2012 (next to be held 2019); prime minister appointed by the presidentelection results: Macky SALL elected president; percent of votes in a runoff - Macky SALL 65.8%, Abdoulaye WADE 34.2%Legislative branch:unicameral National Assembly or Assemblee Nationale (150 seats; 90 members elected by direct popular vote and 60 elected by proportional representation from party lists to serve five-year terms)elections: National Assembly - last held on 1 July 2012 (next to be held in 2017)election results: National Assembly results - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Benno Bokk Yakaar coalition 119, PDS 12, Bokk Giss Giss coalition 4, MCRN-Bes Du Nakk 4, PVD 2, MRDS 2, URD 1, AJ/PADS 1, other 5Judicial branch:highest court(s): Highest Appeals Court or Cour de Cassation (consists of 13 judges including the court president); Constitutional Council (consists of 5 members including the court president, vice-president, and 3 judges)judge selection and term of office: Highest Appeals Court judges' tenure NA; Constitutional Council members appointed by the president of the republic to serve 6-year terms with renewal of 3 members every two yearssubordinate courts: Court of Appeals; regional and first instance courtsPolitical parties and leaders:African Party of Independence [Majhemout DIOP]Alliance for the Republic-Yakaar [Macky SALL]Alliance of Forces of Progress or AFP [Moustapha NIASSE]And-Jef/African Party for Democracy and Socialism or AJ/PADS [Landing SAVANE]Benno Bokk Yakaar coaltion [Macky SALL]Benno Siggil Senegal (a coalition of opposition parties)Bokk Giss Giss coalition [Pape DIOP]Citizen Movement for National Reform or MCRN-Bes Du NakkDemocratic League-Labor Party Movement or LD-MPT [Dr. Abdoulaye BATHILY]Front for Socialism and Democracy/Benno Jubel or FSD/BJ [Cheikh Abdoulaye Bamba DIEYE]Gainde Centrist Bloc or BGC [Jean-Paul DIAS]Independence and Labor Party or PIT [Amath DANSOKHO]Jef-Jel [Talla SYLLA]National Democratic Rally or RND [Madior DIOUF]Party for Truth and Development or PVD [Ahmadou Kara MBACKE]People's Labor Party or PTP [El Hadji DIOUF]Reform Party or PR [Abdourahim AGNE]Republican Movement for Socialism and Democracy or MRDSRewmi Party [Idrissa SECK]Senegalese Democratic Party or PDS [Abdoulaye WADE]Socialist Party or PS [Ousmane Tanor DIENG]SOPI Coalition [Abdoulaye WADE] (a coalition led by the PDS)Synergy for Ethics and Transparency [Aminata TALL]Union for Democratic Renewal or URD [Djibo Leyti KA]Political pressure groups and leaders:other: labor; students; Sufi brotherhoods, including the Mourides and Tidjanes; teachersInternational organization participation:ACP, AfDB, AU, CD, CPLP (associate), ECOWAS, FAO, FZ, G-15, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WADB (regional), WAEMU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Cheikh NIANGchancery: 2031 Florida Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20009telephone: [1] (202) 234-0540FAX: [1] (202) 332-6315consulate(s) general: Houston, New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Lewis LUKENSembassy: Route des Almadies, Dakarmailing address: B. P. 49, Dakartelephone: [221] 33-879-4000FAX: [221] 33-822-2991Flag description:three equal vertical bands of green (hoist side), yellow, and red with a small green five-pointed star centered in the yellow band; green represents Islam, progress, and hope; yellow signifies natural wealth and progress; red symbolizes sacrifice and determination; the star denotes unity and hopenote: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia; the colors from left to right are the same as those of neighboring Mali and the reverse of those on the flag of neighboring GuineaNational symbol(s):lionNational anthem:name: ""Pincez Tous vos Koras, Frappez les Balafons"" (Pluck Your Koras, Strike the Balafons)lyrics/music: Leopold Sedar SENGHOR/Herbert PEPPERnote: adopted 1960; the lyrics were written by Leopold Sedar SENGHOR, Senegal's first president; the anthem is sometimes played incorporating the Koras (harp-like stringed instruments) and Balafons (types of xylophones) mentioned in the titleEconomy ::SenegalEconomy - overview:Senegal relies heavily on donor assistance and foreign direct investment. The country's key export industries are phosphate mining, fertilizer production, and commercial fishing. The country is also working on iron ore and oil exploration projects. After seeing its economy contract by 2.1% in 1993, Senegal made an important turnaround, thanks to an economic reform program backed by the donor community, which led to real growth in GDP averaging over 5% annually during 1995-2007. Annual inflation was pushed down to the single digits. The global economic downturn reduced growth to 2.2% in 2009. The IMF completed a non-dispersing, Policy Support Initiative program in 2010 and approved a new three-year policy support instrument in December 2010 to assist with economic reforms. Senegal also receives disbursements from a $540 million Millennium Challenge Account for infrastructure and agriculture development. In 2012, the economy began to rebound after a weak 2011. The economy continues to suffer from unreliable power supply, which has led to public protests and high unemployment and has prompted migrants to flee Senegal in search of better job opportunities in Europe.GDP (purchasing power parity):$27.01 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 118$26.09 billion (2011 est.)$25.42 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$13.86 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:3.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 972.6% (2011 est.)4.3% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$2,100 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 193$2,000 (2011 est.)$2,000 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:16.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9217.5% of GDP (2011 est.)21.4% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 80.2%government consumption: 6.9%investment in fixed capital: 25.5%investment in inventories: 4.2%exports of goods and services: 28.4%imports of goods and services: -45.1%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 15.2%industry: 22.6%services: 62.2% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:peanuts, millet, corn, sorghum, rice, cotton, tomatoes, green vegetables; cattle, poultry, pigs; fishIndustries:agricultural and fish processing, phosphate mining, fertilizer production, petroleum refining; iron ore, zircon, and gold mining, construction materials, ship construction and repairIndustrial production growth rate:0.1% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 133Labor force:5.906 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 77.5%industry and services: 22.5% (2007 est.)Unemployment rate:48% (2007 est.)country comparison to the world: 193Population below poverty line:54% (2001 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 2.5%highest 10%: 30.1% (2005)Distribution of family income - Gini index:41.3 (2001)country comparison to the world: 5441.3 (1995)Budget:revenues: $3.359 billionexpenditures: $4.213 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:24.2% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 131Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-6.2% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 180Public debt:36.1% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 10035.6% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):1.4% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 253.4% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:0.25% (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 904.25% (31 December 2009 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:14.3% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 4914.5% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$3.577 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 108$3.254 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$5.818 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 122$5.35 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$4.509 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 121$4.186 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$NACurrent account balance:-$1.298 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 120-$1.685 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$2.382 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 138$2.413 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:fish, groundnuts (peanuts), petroleum products, phosphates, cottonExports - partners:Mali 14.4%, Switzerland 14.1%, India 11.9%, France 4.7%, Guinea 4.2% (2012)Imports:$5.733 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 124$5.392 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:food and beverages, capital goods, fuelsImports - partners:France 16.2%, Nigeria 12.9%, India 6.3%, China 6.3%, UK 4.6% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$2.082 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 120$1.946 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$4.222 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 128$4.32 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XOF) per US dollar -510.53 (2012 est.)471.87 (2011 est.)495.28 (2010)472.19 (2009)447.81 (2008)Energy ::SenegalElectricity - production:2.608 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 130Electricity - consumption:2.123 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 139Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 126Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 129Electricity - installed generating capacity:638,000 kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 130Electricity - from fossil fuels:99.7% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 173Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 196Electricity - from other renewable sources:0.3% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 81Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 179Crude oil - imports:13,040 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 183Refined petroleum products - production:16,850 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 97Refined petroleum products - consumption:40,600 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 108Refined petroleum products - exports:7,046 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Refined petroleum products - imports:16,700 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 110Natural gas - production:50 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Natural gas - consumption:50 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 108Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 175Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 126Natural gas - proved reserves:NA cu mCarbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:6.679 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 113Communications ::SenegalTelephones - main lines in use:346,400 (2011)country comparison to the world: 110Telephones - mobile cellular:9.353 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 79Telephone system:general assessment: good system with microwave radio relay, coaxial cable and fiber-optic cable in trunk systemdomestic: above-average urban system with a fiber-optic network; nearly two-thirds of all fixed-line connections are in Dakar where a call-center industry is emerging; expansion of fixed-line services in rural areas needed; mobile-cellular service is expanding rapidlyinternational: country code - 221; the SAT-3/WASC fiber-optic cable provides connectivity to Europe and Asia while Atlantis-2 provides connectivity to South America; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2010)Broadcast media:state-run Radiodiffusion Television Senegalaise (RTS) operates 2 TV stations; a few private TV subscription channels rebroadcast foreign channels without providing any local news or programs; RTS operates a national radio network and a number of regional FM stations; many community and private-broadcast radio stations are available; transmissions of at least 2 international broadcasters are accessible on FM in Dakar (2007)Internet country code:.snInternet hosts:237 (2012)country comparison to the world: 197Internet users:1.818 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 76Transportation ::SenegalAirports:20 (2013)country comparison to the world: 136Airports - with paved runways:total: 9over 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 6914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 111,524 to 2,437 m: 7914 to 1,523 m: 3under 914 m:1 (2013)Pipelines:gas 43 km; refined products 8 km (2013)Railways:total: 906 kmcountry comparison to the world: 92narrow gauge: 906 km 1.000-m gauge (2008)Roadways:total: 14,008 kmcountry comparison to the world: 124paved: 4,099 km (includes 7 km of expressways)unpaved: 9,909 km (2003)Waterways:1,000 km (primarily on the Senegal, Saloum, and Casamance rivers) (2012)country comparison to the world: 64Merchant marine:total: 1country comparison to the world: 150by type: passenger/cargo 1 (2010)Ports and terminals:DakarMilitary ::SenegalMilitary branches:Senegalese Armed Forces: Army, Senegalese National Navy (Marine Senegalaise, MNS), Senegalese Air Force (Armee de l'Air du Senegal) (2013)Military service age and obligation:18 years of age for voluntary military service; 20 years of age for selective conscript service; service obligation is 2 years; women have been accepted into military service since 2008 (2013)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 2,699,196females age 16-49: 3,018,565 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 1,788,493females age 16-49: 2,133,370 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 145,509female: 145,064 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:1.6% of GDP (2011)country comparison to the world: 89Transnational Issues ::SenegalDisputes - international:The Gambia and Guinea-Bissau attempt to stem separatist violence, cross border raids, and arms smuggling into their countries from Senegal's Casamance region, and in 2006, respectively accepted 6,000 and 10,000 Casamance residents fleeing the conflict; 2,500 Guinea-Bissau residents fled into Senegal in 2006 to escape armed confrontations along the borderRefugees and internally displaced persons:refugees (country of origin): 13,702 (Mauritania) (2012)IDPs: 10,000-40,000 (clashes between government troops and separatists in Casamance region) (2012)Illicit drugs:transshipment point for Southwest and Southeast Asian heroin and South American cocaine moving to Europe and North America; illicit cultivator of cannabis"
The World Factbook. 2014.
